- Draw the diagram of forces of a kite
let determine the aerodynamic thrust of the windl on the
kite.
-
|
|
The diagram also lets better
understanding of the behavior of the kite. |
- FORCES AT EQUILIBRIUM
-
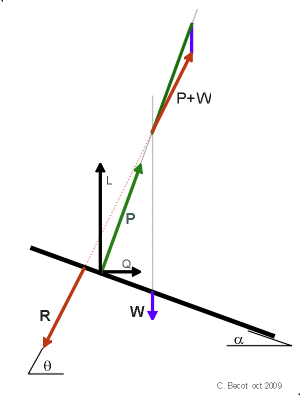
- Here is the general arrangement
of the forces of a kite. The forces as shown are the resultants
of all forces. However, some may prefer to draw apart the
forces of a tail or a drogue.
-
- These forces are when the kite is
at equilibrium
-
- R is the retaining force on the line
- P is the thrust of the wind
- which
components are lift L and drag Q
- W is the weight
-
- a
is the incidence angle of the kite
- q
is the line angle at the bridle.
-
- To
be successful, it must be set up:
- –
the incidence angle a,
- –
the pull on the line, R
- –
the line angle q
- –
the weight of kite, W
- –
the position of the center of gravity.
- -
the bridle point
-
|
|
-
|
- MEASURES ON THE FIELD
- ¤
Fly the kite at 20/30m
- ¤
Measure the line angle
- ¤
Let's walk leeward until being aligned with the outline
of the kite and measure the incidence angle
-
|
|
- MEASURES
AT HOME
-
- ¤
Scale the kite.
- ¤
Hold the kite by the bridle ring. The vertical from the
ring gives the center of gravity on the spine.
- The
spine on cellular kites is through the center of the cells.
|
- DRAW THE DIAGRAMME
- ¤
Draw the spine and the bridle
- ¤
Incline at incidence angle
-
-
|
|


|
|
|
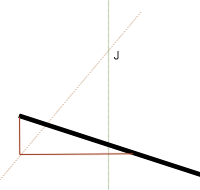
- ¤
Draw the vertical through the center of gravity
- ¤
Draw the line through the bridle ring inclined as the line
angle.
- These
two lines intersects at J.
|
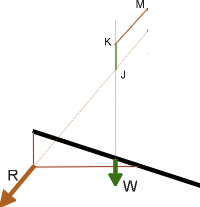
- ¤
Draw the vectors
- –
on the vertical line JK = W
- –
on the oblique line KM = R
|
|
|
|
|
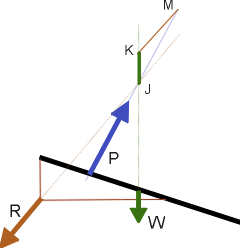
¤ From M draw MJ and extend until the spine
¤
Show the aerodynamic thrust P = JM.
Graphically,
size P, its location on the spine, its inclination. |